Thyroid Volume Calculator
References:
- Lyshchik A, Drozd V, Reiners C. Accuracy of three-dimensional ultrasound for thyroid volume measurement in children and adolescents. Thyroid. 2004 Feb;14(2):113-20. doi: 10.1089/105072504322880346. PMID: 15068625.
- van Isselt JW, de Klerk JM, van Rijk PP, van Gils AP, Polman LJ, Kamphuis C, Meijer R, Beekman FJ. Comparison of methods for thyroid volume estimation in patients with Graves' disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003 Apr;30(4):525-31. doi: 10.1007/s00259-002-1101-1. Epub 2003 Jan 23. PMID: 12541136.
- Brunn J, Block U, Ruf G, Bos I, Kunze WP, Scriba PC. Volumetrie der Schilddrüsenlappen mittels Real-time-Sonographie [Volumetric analysis of thyroid lobes by real-time ultrasound (author's transl)]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1981 Oct 9;106(41):1338-40. German. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1070506. PMID: 7274082.
Related Calculators:
More about the Thyroid Volume Calculator
Why Thyroid Volume Matters
Accurate measurement of thyroid volume is essential for evaluating goiter, monitoring thyroid nodules, planning radioiodine therapy, and assessing the impact of thyroid diseases such as Graves’ disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, and multinodular goiter. Ultrasound-based volume estimation is the most reliable and noninvasive method available, offering rapid and reproducible results that can be easily integrated into routine clinical practice.
Methods Used in This Thyroid Volume Calculator
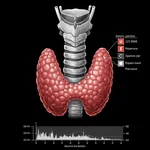
Our thyroid volume calculator provides two widely used and validated methods for estimating thyroid size from ultrasound measurements: the ellipsoid method and the Brunn method (also known as the WHO/Brunn formula). These allow for flexibility and consistency depending on clinical preference or institutional protocols.
1. Ellipsoid Method (Recommended)
The ellipsoid formula is the most commonly used and endorsed approach for calculating thyroid volume in clinical settings. It approximates each thyroid lobe as an ellipsoid using three orthogonal measurements: length (L), width (W), and depth (D), typically acquired in longitudinal and transverse ultrasound planes.
Volume of one lobe = L × W × D × 0.52
The total thyroid volume is the sum of both lobes; the isthmus is typically excluded unless significantly enlarged. This method is simple, practical, and closely aligns with CT or MRI-derived volumetric measurements. It is especially useful for pre- and post-treatment assessments and in thyroid cancer surveillance.
2. Brunn Method (WHO Method)
The Brunn method, proposed by Brunn et al. and widely adopted by the World Health Organization (WHO), is another validated approach for estimating thyroid volume using ultrasound. It uses a slightly different multiplication constant to reflect shape adjustments based on cadaveric correlation studies.
Volume of one lobe = L × W × D × 0.479
Although slightly less commonly used today, the Brunn formula is particularly valuable in epidemiological studies and in historical comparisons where this method was the standard. It remains relevant for global goiter monitoring programs and comparative research.
Clinical Utility of the Thyroid Volume Calculator
Measuring thyroid volume supports a wide range of diagnostic and therapeutic decisions, including:
- Determining the presence and severity of goiter
- Monitoring thyroid size over time or in response to therapy
- Calculating individualized doses of radioactive iodine
- Evaluating mass effect symptoms or tracheal compression
- Guiding surgical planning for thyroidectomy
Normal Reference Values
While normal thyroid volume varies by age, sex, body size, and iodine status, the general upper limits are:
- Women: Up to 18 mL
- Men: Up to 25 mL
- Children: Age-dependent reference charts should be used
Any significant deviation from these values may indicate thyroid pathology and warrant further investigation.
Conclusion
The thyroid volume calculator offers a fast, standardized, and accurate tool for evaluating thyroid gland size using either the ellipsoid or Brunn method. By supporting both traditional and modern techniques, it ensures compatibility with clinical guidelines, research protocols, and global monitoring standards. This calculator empowers clinicians to make more informed decisions in thyroid care, from everyday practice to long-term disease management.