TIRADS Calculator & Report Generator
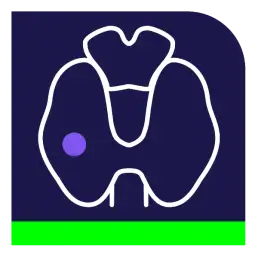
ACR TIRADS flowchart used in this calculator
Related Calculators:
More about the ACR TI-RADS Calculator
This calculator is designed to assist radiologists and trainees in assessing thyroid nodule risk using the American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (ACR TI-RADS)[1]. This thyroid ultrasound scoring system provides a structured framework for evaluating nodules and estimating malignancy risk, making it a valuable tool for clinical decision-making. By combining sonographic features into a cumulative score, the calculator supports evidence-based recommendations for biopsy or surveillance and streamlines thyroid nodule risk assessment in everyday practice.
The clinical management of thyroid nodules has evolved significantly with the widespread adoption of the American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (ACR TI-RADS). Designed to address the high prevalence of incidental thyroid nodules detected in up to 68% of high-resolution ultrasound examinations and the associated potential for overdiagnosis, the TI-RADS calculator provides a standardized, quantitative framework for malignancy risk stratification[3].
Unlike European (EU-TIRADS) or Korean (K-TIRADS) systems which rely on pattern recognition, this thyroid ultrasound scoring tool utilizes a point-based methodology[1]. This approach weights individual sonographic features based on their positive predictive value (PPV) for malignancy. By prioritizing high specificity, the thyroid nodule risk calculator aims to significantly reduce the volume of unnecessary fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsies of benign or indolent lesions while maintaining sensitivity for clinically significant disease.
This reference guide details the scoring mechanics, clinical interpretation, reporting nuances, and limitations essential for board-certified radiologists and trainees utilizing the TI-RADS calculator[2].
The Five Ultrasound Feature Categories
The TI-RADS risk assessment derives a cumulative score from five sonographic categories. Points are assigned based on the feature most suspicious for malignancy within each category[2]. This weighted system ensures that high-risk features contribute disproportionately to the total score generated by the thyroid ultrasound scoring tool, accurately reflecting the increased probability of malignancy.
1. Composition
This category assesses the internal architecture of the nodule.
- Cystic or almost completely cystic (0 points): These lesions are benign and require no further scoring.
- Spongiform (0 points): Defined as composed of greater than 50% small cystic spaces, this appearance is highly specific for benignity.
- Mixed cystic and solid (1 point): This applies regardless of the proportion of the solid component, provided it does not meet spongiform criteria.
- Solid or almost completely solid (2 points): This feature carries a higher risk association. For scoring purposes, visual estimation of >95% solid is sufficient.
2. Echogenicity
Echogenicity is evaluated relative to the surrounding thyroid parenchyma and the anterior neck musculature. For mixed nodules, the score is based exclusively on the solid component.
- Anechoic (0 points): Applies to cystic fluid.
- Hyperechoic or Isoechoic (1 point): Increased or similar echogenicity relative to the thyroid parenchyma.
- Hypoechoic (2 points): Less echogenic than thyroid parenchyma.
- Very Hypoechoic (3 points): Less echogenic than the adjacent strap muscles. This is a specific indicator of malignancy and carries significant weight in the TI-RADS calculator.
3. Shape
Shape is assessed exclusively in the transverse (axial) plane.
- Wider-than-tall (0 points): The anteroposterior diameter is less than or equal to the transverse diameter (parallel orientation).
- Taller-than-wide (3 points): The anteroposterior diameter exceeds the transverse diameter (non-parallel orientation). This feature reflects centrifugal growth against tissue planes and is a strong independent predictor of malignancy.
4. Margin
This category evaluates the interface between the nodule and the surrounding tissue.
- Smooth (0 points): Uninterrupted, well-defined border.
- Ill-defined (0 points): The border merges imperceptibly with the thyroid parenchyma. It is critical to distinguish this from an infiltrative margin; ill-defined margins in isolation are generally benign.
- Lobulated or Irregular (2 points): Spiculated or jagged edges, or protrusions into the parenchyma.
- Extrathyroidal Extension (3 points): Frank invasion into adjacent soft tissue or vascular structures. Mere bulging of the capsule does not qualify as extension.
5. Echogenic Foci
Unlike other categories where a single feature is selected, multiple features can be selected in this category, and their points are additive.
- None or Large Comet-tail Artifacts (0 points): V-shaped artifacts >1 mm in depth are typically associated with colloid and benignity.
- Macrocalcifications (1 point): Coarse calcifications with posterior acoustic shadowing.
- Peripheral (Rim) Calcifications (2 points): Calcification along the nodule margin. These should be scrutinized carefully, as complete shadowing may obscure central malignant components.
- Punctate Echogenic Foci (3 points): These correspond to psammomatous calcifications associated with papillary thyroid carcinoma. They are smaller than macrocalcifications and lack the deep V-shaped tail of colloid artifacts.
Clinical Interpretation: TR Categories and Management with the TI-RADS Calculator
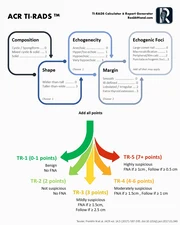
The sum of points determines the TI-RADS (TR) level. This TI-RADS risk assessment score correlates with malignancy risk and dictates size-based management thresholds.
A defining characteristic of the ACR TI-RADS is the intentional use of higher size thresholds for biopsy compared to other international guidelines. This shift is largely driven by the reclassification of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclear Features (NIFTP)[4]. Recognizing NIFTP as an indolent lesion, the ACR established these thresholds to minimize the overtreatment of non-threatening neoplasms, prioritizing clinical significance over mere detection.
| Category | Points | Malignancy Risk | Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| TR1: Benign | 0 | < 0.3% | No FNA required. |
| TR2: Not Suspicious | 2 | ~1.5% | No FNA required. |
| TR3: Mildly Suspicious | 3 | ~4.8% | FNA if ≥ 2.5 cm Follow-up US if ≥ 1.5 cm |
| TR4: Moderately Suspicious | 4-6 | ~9.1% | FNA if ≥ 1.5 cm Follow-up US if ≥ 1.0 cm |
| TR5: Highly Suspicious | ≥ 7 | ~35% | FNA if ≥ 1.0 cm Follow-up US if ≥ 0.5 cm |
Global Context: Comparison with EU-TIRADS and K-TIRADS
While all major risk stratification systems aim to identify thyroid malignancy, they differ fundamentally in their approach and clinical goals.
- Methodology: The TI-RADS calculator employs a point-based system, where specific features are weighted and summed. In contrast, EU-TIRADS (European) and K-TIRADS (Korean) utilize pattern-based systems, where nodules are matched to visual templates or patterns.
- Sensitivity vs. Specificity: The ACR system is optimized for specificity. By setting higher biopsy size thresholds and requiring substantial sonographic evidence to escalate risk, the thyroid nodule risk calculator results in the highest percentage of avoided biopsies among the major guidelines[3]. Conversely, K-TIRADS and EU-TIRADS generally prioritize sensitivity, leading to higher detection rates but a concomitant increase in biopsies of benign nodules.
- The "Blind Spot": Radiologists should be aware that the high specificity of the TI-RADS risk assessment creates a potential "blind spot" for small (1.0-1.5 cm), solid, hyperechoic nodules. These are classified as TR3 and would not undergo biopsy until reaching 2.5 cm under ACR guidelines, whereas other systems might recommend earlier intervention.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How strictly should size thresholds for FNA be applied?
The size thresholds (1.5 cm for TR4 and 1.0 cm for TR5) balance cancer detection with the prevention of overdiagnosis. While strict adherence maintains the system’s high specificity, clinical judgment is paramount. Factors such as patient anxiety, comorbidities, or proximity to critical structures (e.g., trachea, recurrent laryngeal nerve) may justify deviation from the standard TI-RADS risk assessment protocols.
How should partially cystic nodules be scored?
Partially cystic nodules are assigned 1 point for composition ("mixed cystic and solid"). However, points for echogenicity, margins, and echogenic foci should be based exclusively on the appearance of the solid component or the nodule periphery.
Do punctate echogenic foci always represent microcalcifications?
Not always. While punctate foci often represent psammomatous calcifications (highly associated with PTC), they can occasionally represent inspissated colloid. The key discriminator is the absence of a large comet-tail artifact. If uncertain, it is safer to score them as punctate foci (3 points) to ensure appropriate risk stratification.
How is taller-than-wide shape defined in practice?
This feature is defined strictly as the anteroposterior diameter exceeding the transverse diameter when measured in the axial (transverse) plane. Measurements taken in the longitudinal/sagittal plane are not used for this determination in the TI-RADS calculator.
Why does ACR TI-RADS use a point-based system instead of patterns?
The point-based system provides a more objective thyroid ultrasound scoring tool that prioritizes specificity. By assigning weights to features based on their statistical correlation with malignancy, the system reduces the subjectivity inherent in "best-fit" pattern recognition models.
When is surveillance preferred over biopsy?
Surveillance is preferred for nodules that meet the TR level criteria but fall below the size threshold for biopsy (e.g., a 0.8 cm TR5 nodule). Additionally, active surveillance is increasingly accepted for small (<1.0 cm), low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinomas (PTMC) without nodal metastasis or extrathyroidal extension.
How should interval growth be interpreted?
Significant interval growth is defined as a 20% increase in at least two dimensions with a minimum increase of 2 mm, or a 50% increase in volume. If a nodule grows but remains below the FNA threshold for its TR category, the next follow-up is typically scheduled after 1 year.
Can TI-RADS be applied to incidental thyroid nodules?
Yes. ACR TI-RADS was specifically designed to manage the increasing volume of incidental thyroid nodules ("incidentalomas") detected on CT, MRI, or PET scans. Once identified, these nodules should be evaluated with dedicated thyroid ultrasound and scored according to TI-RADS risk assessment criteria.
What is the impact of NIFTP on the guidelines?
The recognition of NIFTP (Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclear Features) as an indolent lesion significantly influenced the ACR guidelines[4]. The higher biopsy thresholds in the thyroid nodule risk calculator aim to avoid over-treating these non-aggressive neoplasms, which previously might have been classified as carcinomas requiring surgery.
References
- Tessler FN, et al. ACR Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS): White Paper of the ACR TI-RADS Committee. J Am Coll Radiol. 2017;14(5):587-595.
- Grant EG, et al. Thyroid Ultrasound Reporting Lexicon: White Paper of the ACR Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System Committee. J Am Coll Radiol. 2015;12(12 Pt A):1272-1279.
- Middleton WD, et al. Multi-institutional Analysis of Thyroid Nodule Risk Stratification Using the American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017;208(6):1331-1341.
- Nikiforov YE, et al. Nomenclature Revision for Encapsulated Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Paradigm Shift to Reduce Overtreatment of Indolent Tumors. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2(8):1023-1029.
All images in this calculator have been obtained from ACR's TI-RADS atlas. Click here to download the full document for TI-RADS from ACR's website.





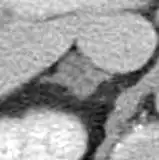


Hi there,
I just used the TI-RADS calculator for a nodule with the following charactristics:
Nodule #1:
– Location: left lobe (mid segment)
– Size: 0.7 cm
– Composition: Solid or almost completely solid
– Echogenicity: Hypoechoic
– Shape: Wider than tall
– Margins: Smooth
– Additional findings: Peripheral/rim calcifications
And it has classed the nodule as TR 4 rather than 5.
Really appreciate the tool 🙂
Hello Orla,
Thanks for your feedback. Based on the characteristics you listed: solid (2), hypoechoic (2), peripheral/rim calcifications (2), smooth margins (0), wider than tall (0), the total comes to 6 points, which corresponds to TR-4. Could you clarify which feature you counted that led to TR-5?
What an incredibly helpful tool! Thank you!