NASCET Calculator (+ECST) for Carotid Artery Stenosis
This calculator uses measurements of CTA and MRA
References:
- North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators, Barnett, H. J. M., Taylor, D. W., Haynes, R. B., Sackett, D. L., Peerless, S. J., Ferguson, G. G., Fox, A. J., Rankin, R. N., Hachinski, V. C., Wiebers, D. O., & Eliasziw, M. (1991). Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade carotid stenosis. The New England journal of medicine, 325(7), 445–453. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199108153250701
- Randomised trial of endarterectomy for recently symptomatic carotid stenosis: final results of the MRC European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST). (1998). Lancet (London, England), 351(9113), 1379–1387.
Related Calculators:
More about the ECST & NASCET Calculator:
Overview of NASCET and ECST
The North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET) and the European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST) have served as foundational studies in the evaluation and management of internal carotid artery (ICA) stenosis. These landmark trials provided robust, evidence-based support for carotid endarterectomy (CEA) in symptomatic patients and significantly shaped modern stroke prevention protocols. Accurate quantification of ICA stenosis, as outlined by the NASCET and ECST methodologies, remains a cornerstone of vascular imaging and interventional decision-making.
The NASCET Trial: Impact and Methodology
NASCET was a randomized, multicenter trial conducted in the United States and Canada that focused on patients with recent hemispheric transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), amaurosis fugax, or nondisabling ischemic strokes. The study demonstrated that CEA significantly reduced the risk of recurrent ipsilateral stroke in patients with high-grade ICA stenosis (70–99%). Specifically, the two-year risk of ipsilateral stroke was 26% in patients managed medically versus only 9% in those treated with surgery, resulting in a 17% absolute risk reduction and nearly 65% relative risk reduction. The benefit was even greater when considering major or fatal strokes, with an absolute reduction of 10.6%.
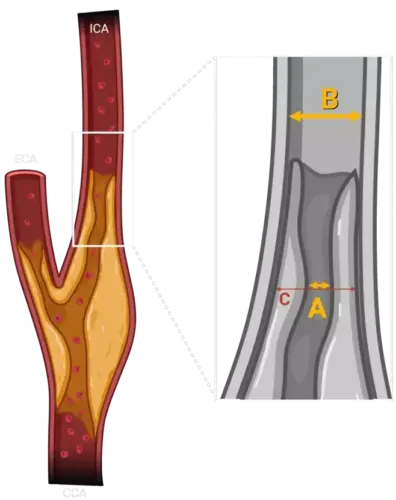
The NASCET method calculates stenosis using the diameter of the narrowest portion of the artery and comparing it to the normal distal ICA diameter, just beyond the carotid bulb:
Stenosis (%) = [(1 - (narrowest diameter / distal ICA diameter)) × 100]
This standardized measurement approach provides consistency and reproducibility across imaging modalities such as CT angiography (CTA) and MR angiography (MRA).
The ECST Trial: European Perspective
The ECST, conducted in Europe, approached stenosis measurement differently by estimating the original (pre-disease) diameter of the artery at the lesion site. Though this often resulted in higher numeric values for the same anatomical narrowing compared to NASCET, the trial similarly confirmed the life-saving potential of CEA. For patients with greater than 80% stenosis, the three-year risk of major stroke or death was 14.9% in the surgery group versus 26.5% in the control group, yielding an absolute risk reduction of 11.6%.
Both NASCET and ECST demonstrated that timely intervention for high-grade stenosis can dramatically improve patient outcomes, reinforcing the importance of accurate stenosis quantification.
Why Use the NASCET & ECST Calculators?
The NASCET calculator is designed to bring the precision of these landmark trials into everyday clinical use. They provide automatic, evidence-based calculations of ICA stenosis using either NASCET or ECST criteria, offering the following advantages:
- Standardized Assessment: Apply consistent measurement formulas validated by clinical trials.
- Improved Workflow Efficiency: Automate calculations, saving time in busy clinical environments.
- Enhanced Communication: Provide objective, easy-to-understand numbers to support shared decision-making with patients.
- Support for Multidisciplinary Teams: Align neurologists, radiologists, and vascular surgeons around a common risk stratification framework.
Expanded Clinical Utility
While originally developed to evaluate candidates for carotid endarterectomy, these tools also support modern approaches to carotid artery stenting (CAS), especially in patients with high surgical risk. They are valuable in evaluating both symptomatic and select asymptomatic patients with high-grade stenosis, helping guide nuanced treatment decisions in borderline or individualized cases.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite their utility, these calculators are not substitutes for clinical judgment. They depend on the quality of imaging and accuracy of diameter measurements. Additional factors—such as plaque morphology, patient comorbidities, life expectancy, and surgical/anesthetic risk—must be considered alongside calculator output. As imaging technology and stroke prevention strategies evolve, thresholds and recommendations may also shift over time.
Conclusion: Evidence Meets Practicality
The NASCET and ECST calculators embody the integration of landmark research, radiologic precision, and practical usability. They empower clinicians with reproducible, objective tools to guide life-saving decisions in neurovascular care. By embedding them into routine workflows, we help ensure that patient management is grounded in the best available evidence, ultimately advancing stroke prevention and improving clinical outcomes. Please note that NASCET and ECST are names of clinical trials and are not affiliated with or endorsed by this tool. NASCET was supported by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) through the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). ACR® is a registered trademark of the American College of Radiology.




this was the best nascet calculator that i saw but no longer works. not showing the % stenosis. shame
Thank you for your feedback. Over the past few days, we have encountered occasional and temporary issues due to the relocation and upgrade of our servers. I expect the website to stabilize within a day or two. Thank you for your patience.
glad to see it back up and running. the other calculators were okay but you have to click calculate instead of doing it automatically