Spleen Volume & Splenic Index Calculator for US, CT, and MRI
References:
- Chow KU, Luxembourg B, Seifried E, Bonig H. Spleen Size Is Significantly Influenced by Body Height and Sex: Establishment of Normal Values for Spleen Size at US with a Cohort of 1200 Healthy Individuals. Radiology. 2016;279(1):306-313. doi:10.1148/radiol.2015150887
- Yetter EM, Acosta KB, Olson MC, Blundell K. Estimating splenic volume: sonographic measurements correlated with helical CT determination. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;181(6):1615-1620. doi:10.2214/ajr.181.6.1811615
Related Calculators:
More about the spleen volume and splenic index calculator:
The spleen plays a pivotal role in hematologic and immune function, making its size and volume critical metrics in evaluating a wide array of medical conditions. Splenic index and volume measurements are indispensable for diagnosing and managing disorders such as splenomegaly, portal hypertension, and hematologic malignancies. These parameters also help identify systemic and infectious conditions that impact spleen size and functionality. Our advanced calculators offer healthcare professionals an efficient, accurate, and user-friendly tool to estimate these parameters using detailed imaging data, enhancing diagnostic accuracy, clinical decision-making, and patient care quality.
Accurate calculation of splenic index and volume is essential for tracking disease progression, evaluating treatment responses, and identifying complications early. By employing validated algorithms and evidence-based formulas, our calculators ensure reliable and consistent results. These tools streamline patient evaluation workflows, enabling healthcare providers to focus on critical aspects of patient care while maintaining precision and efficiency.
Spleen Volume Calculator
Spleen volume is a vital parameter in modern clinical practice, offering critical insights into splenic involvement in numerous diseases. An enlarged spleen (splenomegaly) may indicate conditions such as cirrhosis, lymphoma, infections, or hematologic disorders, while a smaller-than-normal spleen may suggest congenital anomalies or post-treatment changes. Our calculator utilizes cutting-edge methodologies to provide precise and reproducible results, ensuring high accuracy for both routine assessments and advanced diagnostics. The use of these calculators supports consistency in evaluations and minimizes the risk of diagnostic errors.
Why Spleen Volume Matters
Measuring spleen volume is a cornerstone of clinical diagnostics, particularly for conditions like splenomegaly, which is often associated with systemic illnesses such as liver disease and portal hypertension. Accurate volume measurements can also provide valuable information about disease severity, guide therapeutic interventions, and monitor treatment outcomes over time. Common methods used for spleen volume estimation include:
1. Ellipsoid Formula
The ellipsoid formula approximates spleen volume by treating the organ as an ellipsoid and measuring its three primary dimensions: length, width, and thickness. This approach is widely favored for its simplicity, speed, and practicality in clinical settings. While the formula may slightly underestimate spleen size compared to advanced volumetric techniques, it remains a reliable and efficient tool for everyday use, particularly when quick assessments are needed.
2. Planimetric Methods
Planimetry, considered the gold standard for spleen volume measurements, involves manual segmentation of the spleen on cross-sectional imaging studies. Although this method offers unparalleled accuracy, its time-intensive nature often limits its use to research settings or complex diagnostic scenarios. Despite these limitations, planimetric methods remain invaluable for providing highly detailed and accurate spleen volume assessments.
Splenic Index Calculator
The splenic index is a calculated metric that combines spleen dimensions to provide a standardized measure of organ size. This index is particularly useful for population studies, allowing for comparisons across demographic groups, and for longitudinal monitoring of spleen size changes over time. It is also a critical tool in distinguishing between normal and abnormal spleen sizes in diverse clinical contexts.
Diagnostic Applications
Precise splenic index and volume calculations are vital for diagnosing and managing a broad spectrum of medical conditions. These metrics are instrumental in evaluating splenomegaly, guiding therapeutic strategies for portal hypertension, and monitoring treatment efficacy in conditions such as hematologic malignancies. They are also valuable in detecting splenic infarctions, focal lesions, or structural abnormalities associated with systemic diseases, providing critical information for comprehensive patient management.
Imaging Modalities
Advanced imaging techniques, including computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound, are commonly employed for splenic index and volume measurements. CT and MRI are renowned for their accuracy and reproducibility, making them the preferred modalities for detailed evaluations. Ultrasound, while less precise than CT and MRI, offers a practical, cost-effective, and non-invasive option, particularly in resource-limited settings. Recent innovations in 3D ultrasound technology have significantly enhanced its accuracy, making it an increasingly viable choice for clinical and research applications.
Comparison of Techniques
Comparative analyses of spleen measurement methods highlight a balance between practicality and precision. While the ellipsoid formula provides a quick and reasonably accurate estimation suitable for routine clinical use, planimetric and other advanced volumetric approaches deliver higher precision, making them invaluable for research and complex diagnostic scenarios. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each method is essential for selecting the most appropriate technique based on clinical needs and resource availability.
Ultrasound-Based Studies
Ultrasound remains one of the most widely used imaging modalities for spleen size assessment due to its accessibility and cost-effectiveness. Traditional 2D ultrasound techniques are commonly employed, but the advent of 3D ultrasound has markedly improved measurement precision. This advancement enhances the applicability of ultrasound for routine clinical evaluations and specialized research purposes, ensuring a balance between affordability, convenience, and accuracy.
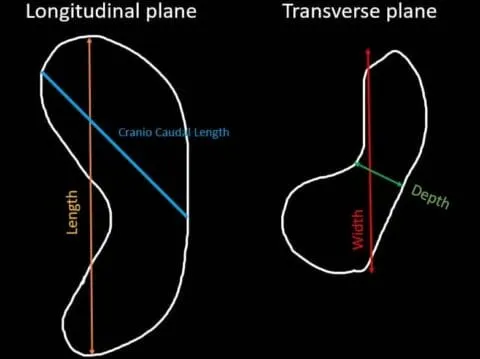
Splenic Index = ML x W x T
Volume = π/6 × ML × W × D
Revised formula² for Splenic Volume using sonographic measurements = π/6 × W × D × ((ML + CCL) / 2)
Expected volume/length based on sex and height is derived from the formula by Chow et al.¹
Parameters:
ML = Maximum Length
CCL = Craniocaudal Length (most superior to most inferior aspect)
W = Width
D = Depth
Our calculators are backed by robust and validated methodologies, ensuring accurate, reliable, and clinically relevant results. For detailed insights into the underlying methodologies, applications, and research that support these tools, please refer to the references provided above.